Micropython API reference: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
| Get the values from the 8 proximity sensors. Higher values indicate a closer object. | | Get the values from the 8 proximity sensors. Higher values indicate a closer object. | ||
| <code>list</code> (of 8 integers) | | <code>list</code> (of 8 integers) | ||
|- | |||
| <code>epuck2.button_pressed()</code> | |||
| None | |||
| Get button state. | |||
| <code>True if pressed</code> | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 27 November 2025
The following figures show the main components offered by the e-puck2 robot and where they are physically placed:
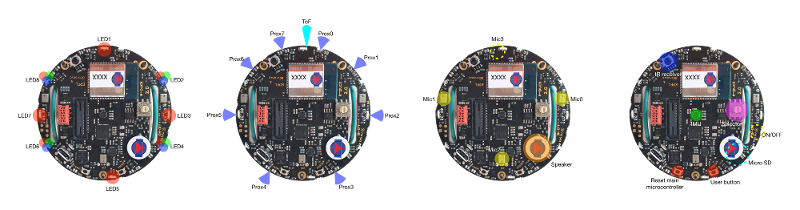
1 Functions list
| Method | Parameters | Description | Returns |
|---|---|---|---|
epuck2.get_api_version()
|
None | Returns the current e-puck2 API version as a string. | str
|
epuck2.set_rgb()
|
led: int, red: int, green: int, blue: int
|
Set the intensity of a single RGB LED. Intensity ranges between 0 (off) and 100 (full on). | None
|
epuck2.set_all_rgb()
|
red2..blue8: int (12 arguments total)
|
Set the intensity for all four RGB LEDs (LED 2, 4, 6, 8) simultaneously. Intensity ranges between 0 and 100. | None
|
epuck2_set_leds()
|
led1,led3,led5,led7,body,front
|
Set the LEDs state (on, off). | None
|
epuck2.play_sound()
|
sound id
|
Play onboard sound. | None
|
epuck2.set_motors_speed()
|
left: int, right: int
|
Set the speed for the left and right motors. | None
|
epuck2.set_all_actuators()
|
actuators list (17 arguments total)
|
Set all actuators at once. | None
|
epuck2.get_proximity()
|
None | Get the values from the 8 proximity sensors. Higher values indicate a closer object. | list (of 8 integers)
|
epuck2.button_pressed()
|
None | Get button state. | True if pressed
|
2 Various
2.1 epuck2.get_api_version()
Returns the API version as a string (e.g., "02.01").
import epuck2
version = epuck2.get_api_version()
print(version) # Example output: "XX.XX"3 LEDs
3.1 epuck2.set_rgb(led, red, green, blue)
Set the intensity of one of the four RGB LEDs.
Parameters:
*led(int): The index of the LED to control: *0: LED 2 (Front Right) *1: LED 4 (Back Right) *2: LED 6 (Back Left) *3: LED 8 (Front Left) *red,green,blue(int): Intensity from 0 (off) to 100 (full brightness).
Example:
# Set LED 1 (Index 0, LED 2) to half-intensity Blue
import epuck2
epuck2.set_rgb(0, 0, 0, 50)3.2 epuck2.set_all_rgb(red2, green2, blue2, red4, green4, blue4, red6, green6, blue6, red8, green8, blue8)
Sets all four RGB LEDs simultaneously. The arguments are grouped in R, G, B for LEDs 2, 4, 6, and 8 in that order.
Parameters: 12 integers representing the R, G, B values for LED 2, LED 4, LED 6, and LED 8, respectively. All values are in the range 0 to 100.
Example:
# Set LED 2 to Red (100, 0, 0) and LED 4 to Green (0, 100, 0). Other LEDs are off.
import epuck2
epuck2.set_all_rgb(100, 0, 0, # LED 2
0, 100, 0, # LED 4
0, 0, 0, # LED 6
0, 0, 0) # LED 84 Proximity sensors
4.1 epuck2.get_proximity()
Retrieves the proximity sensor readings.
Returns: A list of 8 integers.
Example:
import epuck2
prox_values = epuck2.get_proximity()
# prox_values[0] is sensor S0, prox_values[7] is sensor S7
print(prox_values)5 Motors
5.1 epuck2.set_motors_speed(left, right)
Set the speed of the left and right motors.
Parameters:
*left(int): Speed of the left motor. Range is **-1000** (reverse) to **1000** (forward). *right(int): Speed of the right motor. Range is **-1000** (reverse) to **1000** (forward).
Example:
# Move forward at full speed
import epuck2
epuck2.set_motors_speed(1000, 1000)
# Turn right in place
import epuck2
epuck2.set_motors_speed(500, -500)